Contextualize Alerts
Introduction
CrowdSec doesn't store raw log information once it has finished processing them. However, you can send additional data within an alert with a feature we call alert context:

Whilst some collections already include a context configuration, you must enable the context option within your Security Engine console configuration.
This can be achieved by running:
sudo cscli console enable context
Check current config
These commands have to be run on the CrowdSec Local API
You can view the current status of your console options with:
$ sudo cscli console status
╭────────────────────┬───────────┬───────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ Option Name │ Activated │ Description │
├────────────────────┼───────────┼───────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ custom │ ✅ │ Send alerts from custom scenarios to the console │
│ manual │ ❌ │ Send manual decisions to the console │
│ tainted │ ✅ │ Send alerts from tainted scenarios to the console │
│ context │ ✅ │ Send context with alerts to the console │
│ console_management │ ❌ │ Receive decisions from console │
╰────────────────────┴───────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
You can enable alert context with:
sudo cscli console enable context
You can as well inspect and control the enabled alert context configuration:
$ sudo cscli lapi context status
method:
- evt.Meta.http_verb
status:
- evt.Meta.http_status
target_uri:
- evt.Meta.http_path
target_user:
- evt.Meta.target_user
user_agent:
- evt.Meta.http_user_agent
The context configuration can as well be found in /etc/crowdsec/contexts/ as yaml files.
Vizualise alert context
The alert context will be display when inspecting an alert:
$ sudo cscli alerts inspect 7
################################################################################################
- ID : 7
- Date : 2022-12-12T18:46:44Z
- Machine : c620f52cedf9432e969f26afee12d651
- Simulation : false
- Reason : crowdsecurity/http-bad-user-agent
- Events Count : 2
- Scope:Value: Ip:127.0.0.1
- Country :
- AS :
- Begin : 2022-12-12 18:46:43.339960525 +0000 UTC
- End : 2022-12-12 18:46:43.341210351 +0000 UTC
- Active Decisions :
╭───────┬──────────────┬────────┬────────────────────┬──────────────────────╮
│ ID │ scope:value │ action │ expiration │ created_at │
├───────┼──────────────┼────────┼────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤
│ 15006 │ Ip:127.0.0.1 │ ban │ 3h59m50.949157024s │ 2022-12-12T18:46:44Z │
╰───────┴──────────────┴────────┴────────────────────┴──────────────────────╯
- Context :
╭─────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ Key │ Value │
├─────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ target_fqdn │ www.crowdsec-test.net │
│ target_fqdn │ www.crowdsec-test-1.net │
│ user_agent │ Mozilla/5.00 (Nikto/2.1.5) (Evasions:None) (Test:Port Check) │
│ user_agent │ Mozilla/5.00 (Nikto/2.1.5) (Evasions:None) (Test:getinfo) │
╰─────────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
And we can see that the target_fqdn and the user_agent are now displayed in the context of the alert.
Adding custom alert context
You can get context values from:
- Part of a parsed log line (with
evt.Parsed) - Meta values set by parsers (with
evt.Meta) - Hardcoded strings in the context configuration (with
"my_value") - More generally, anything available in
evt(eg,evt.Unmarshaledwith some parsers) - From expr helpers (all expr helpers are available in the context, allowing for example
CrowdsecCTI(evt.Meta.source_ip).GetMaliciousnessScore())
You can add your custom alert context by adding a yaml file in /etc/crowdsec/contexts/ :
cat > /etc/crowdsec/contexts/example.yaml << EOF
context:
example_value:
- '"something"'
http_extra_status:
- evt.Meta.http_status
EOF
Let's now trigger a http scenario by trying to exploit a well known vulnerability:
$ curl 'target.com/%2E%2E/%2E%2E'
In crowdsec.log, we're seeing our alert:
time="2024-01-24T18:08:34+01:00" level=info msg="Ip x.x.x.x performed 'crowdsecurity/http-cve-2021-41773' (1 events over 336ns) at 2024-01-24 17:08:34.026228434 +0000 UTC"
It as well appears when we're inspecting our alert:
$ cscli alerts list
╭──────┬────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────────────────┬─────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┬───────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ ID │ value │ reason │ country │ as │ decisions │ created_at │
├──────┼────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────────────────┼─────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┼───────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────┤
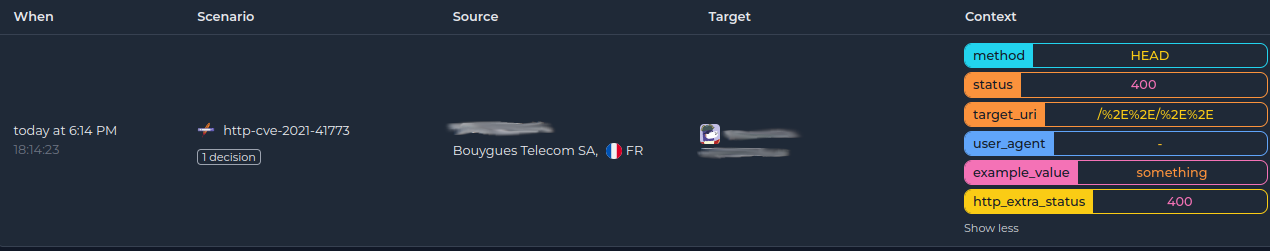
│ 6545 │ Ip:xxx.xx.xx.xx │ crowdsecurity/http-cve-2021-41773 │ FR │ 5410 Bouygues Telecom SA │ ban:1 │ 2024-01-24 17:08:34.026228866 +0000 UTC │
...
$ cscli alerts inspect -d 6545
...
- Context :
╭───────────────────┬────────────────╮
│ Key │ Value │
├───────────────────┼────────────────┤
│ example_value │ something │
│ http_extra_status │ 400 │
│ method │ HEAD │
│ status │ 400 │
│ target_uri │ /%2E%2E/%2E%2E │
│ user_agent │ - │
╰───────────────────┴────────────────╯
...
And in the console:
More information here for managing the context from the Hub with cscli.
Automagically detect possible alert context
It is possible to detect all the possible fields that a given parser can output (or all the installed parsers with --all flag):
$ sudo cscli lapi context detect crowdsecurity/nginx-logs
Acquisition :
- evt.Line.Module
- evt.Line.Raw
- evt.Line.Src
crowdsecurity/nginx-logs :
- evt.Meta.http_path
- evt.Meta.http_status
- evt.Meta.http_user_agent
- evt.Meta.http_verb
- evt.Meta.log_type
- evt.Meta.service
- evt.Meta.source_ip
- evt.Meta.target_fqdn
- evt.Parsed.body_bytes_sent
- evt.Parsed.cid
- evt.Parsed.http_referer
- evt.Parsed.http_user_agent
- evt.Parsed.http_version
- evt.Parsed.loglevel
- evt.Parsed.message
- evt.Parsed.pid
- evt.Parsed.proxy_alternative_upstream_name
- evt.Parsed.proxy_upstream_name
- evt.Parsed.remote_addr
- evt.Parsed.remote_user
- evt.Parsed.request
- evt.Parsed.request_length
- evt.Parsed.request_time
- evt.Parsed.status
- evt.Parsed.target_fqdn
- evt.Parsed.tid
- evt.Parsed.time
- evt.Parsed.time_local
- evt.Parsed.verb
- evt.StrTime
Delete a context
Delete the yaml file containing your custom alert context, and reload crowdsec.
rm /etc/crowdsec/contexts/example.yaml
systemctl restart crowdsec

