Firewall
📚 Documentation 💠 Hub 💬 Discourse
CrowdSec Remediation Component written in golang for firewalls.
crowdsec-firewall-bouncer will fetch new and old decisions from a CrowdSec API and add them to a blocklist used by supported firewalls.
Supported firewalls:
- iptables (IPv4 ✔️ / IPv6 ✔️ )
- nftables (IPv4 ✔️ / IPv6 ✔️ )
- ipset only (IPv4 ✔️ / IPv6 ✔️ )
- pf (IPV4 ✔️ / IPV6 ✔️ )
Installation
Packages for crowdsec-firewall-bouncer are available on our repositories. You need to pick the package according to your firewall system :
IPTables
- Debian/Ubuntu
- RHEL/Centos/Fedora
sudo apt install crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-iptables
sudo yum install crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-iptables
NFTables
- Debian/Ubuntu
- RHEL/Centos/Fedora
sudo apt install crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-nftables
sudo yum install crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-nftables
pf
- FreeBSD
sudo pkg install crowdsec-firewall-bouncer
See as well Manual Installation documentation below
Configuration
There are two primary ways to use the firewall bouncer:
- managed (default): cs-firewall-bouncer will create ipset/nft sets, insert the associated firewall rules and manage the set contents
- set only: you already have a (complex) firewall setup, cs-firewall-bouncer will only manage the content of existing specified sets
Managed mode : Iptables/ipset or Nftables
This is the default behaviour
In "managed" mode (mode nftables or iptables), component creates all the needed elements (rules, sets) and insert the appropriate rules in nftables or iptables.
IPSet (when using iptables mode) does not support a timeout greater than 2147483 seconds (about 596 hours). If crowdsec is configured to take decisions longer than that, the bouncer will cap the duration to 2147482 seconds.
Set Only : Iptables/Ipset table
In iptables set-only mode (mode ipset), the component only handles the contents of sets that are specified by blacklists_ipv4 and blacklists_ipv6.
These sets must be created before starting the component, and it is the user's responsibility to create the associated iptables rules.
IPSet does not support a timeout greater than 2147483 seconds (about 596 hours). If crowdsec is configured to take decisions longer than that, the bouncer will cap the duration to 2147482 seconds.
Set Only : nftables
In nftables set only mode (mode nftables with nftables.{ipv4,ipv6}.set-only set to true), the component only manages the contents of the sets.
It's the user's responsibility to create the associated chains and sets :
table ip crowdsec {
set crowdsec-blacklists {
type ipv4_addr
flags timeout
}
chain crowdsec-chain {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
ip saddr @crowdsec-blacklists drop
}
}
table ip6 crowdsec6 {
set crowdsec6-blacklists {
type ipv6_addr
flags timeout
}
chain crowdsec6-chain {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
ip6 saddr @crowdsec6-blacklists drop
}
}
Metrics
CrowdSec v1.6.3 and Firewall Remediation Component v0.0.30 are minimum versions required to have metrics.
You can check the metrics generated by the firewall-bouncer using the command cscli metrics show bouncers.
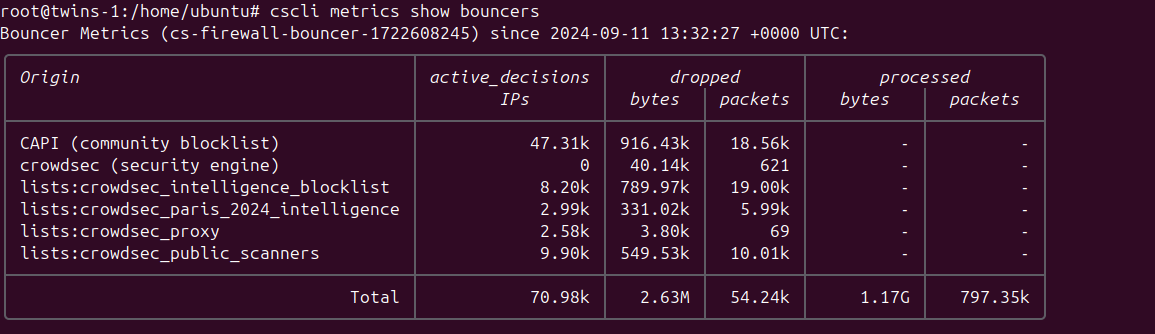
Each line in the output represents a different source of blocked IPs, along with detailed metrics.
Originrefers to the name of the source, which could be:CAPI- The community blocklist that you receive in exchange for the information you provide to the networkcrowdsec (security engine)- The decisions made by your Security Engine based on triggered scenarioslists:*- Various lists to which you are subscribed
active_decisions IPsrepresents the number of IPs contained in the respective listdropped bytes & packetsindicates the number of bytes and packets dropped by the firewall due to the actions of the specified originprocessed bytes & packetsis only present for theTotalline, as it denotes the overall number of bytes and packets processed by your firewall.
As the firewall bouncer operates at the network level, most malicious programs will not progress beyond attempting to establish a connection (and being denied). Therefore, metrics cannot reflect the "potentially saved traffic."
Ipset only mode
If you are running ipset only mode, crowdsec-firewall-bouncer tries parsing the output to produce metrics, but:
- "managed" firewalls such ufw might confuse parser and lead to inconsistent metrics.
- "total" counters amount since the machine start, or iptables counter are reset, which can lead to inconsistent metrics.
Configuration Reference
You can find a default configuration hosted on the Github Repository this is provided with the installation package.
pid_dir
Depreacted
Directory to store the pid file
daemonize
Deprecated
Run the component in the background
This field has now been deprecated and is ignored within the component
mode
iptables|nftables|ipset|pf
Firewall mode to use
update_frequency
string (That is parseable by time.ParseDuration)
Frequency to contact the API for new/deleted decisions
scenarios_containing
[ ]string
Get only IPs banned for triggering scenarios containing either of provided word.
scenarios_containing: ["ssh", "http"]
scenarios_not_containing
[ ]string
Ignore IPs banned for triggering scenarios containing either of provided word.
scenarios_not_containing: ["ssh", "http"]
scopes
[ ]string
Decisions will be filtered on the provided scopes.
scopes: ["Ip", "Range"]
origins
[ ]string
Decisions will be filtered on the provided origins.
origins: ["cscli", "crowdsec"]
log_mode
file|stdout
Where the log contents are written (With file it will be written to log_dir with the name crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.log)
log_dir
string
Log directory path, that will contain the log file
log_level
trace|debug|info|warn|error
Log level
log_compression
true|false
Compress log files on rotation
log_max_size
int (in MB)
Max size of log files before rotation
log_max_backups
int
How many backup log files to keep before deletion (can happen before log_max_age is reached)
log_max_age
int (in days)
Max age of backup files before deletion (can happen before log_max_backups is reached)
api_url
string
URL of the local API EG: http://127.0.0.1:8080
api_key
string
API key to authenticate with the local API
cert_path
string
Path to the client certificate for authentication
key_path
string
Path to the certificate key used with cert_path
ca_cert_path
string
Path to the CA certificate to trust usually used in conjunction with cert_path and key_path
insecure_skip_verify
true|false
Skip verification of the API certificate, typical for self-signed certificates
disable_ipv6
true|false
disable interacting with ipv6 chains/sets, defaults to false
deny_action
DROP|REJECT
firewall action to apply, defaults to DROP
deny_log
true|false
if set to true, enables logging of dropped packets (ie. -j LOG)
deny_log_prefix
string
if logging is true, this sets the log prefix, defaults to "crowdsec: "
Iptables/Ipset specific directives
iptables_chains
[]string
specify a list of chains to insert rules
iptables_chains:
- INPUT
#- FORWARD
#- DOCKER-USER
If you are using a dockerized application and allow remote connections to the exposed port, you need to add the DOCKER-USER chain to the list of chains.
blacklists_ipv4
string
name of the ipv4 set
blacklists_ipv6
name of the ipv6 set
ipset_size
int
maximum number of entries in the ipset (default: 131072)
ipset_type
string
type to use for the set (default: nethash)
The default value for ipset_size has been raised in v0.0.28 (from 65536) to allow for larger blocklists.
Nftables specific directives
Nftables mode has its own nftables section, with sub-section of ipv4 and ipv6 :
## nftables
nftables:
ipv4:
enabled: true
set-only: false
table: crowdsec
chain: crowdsec-chain
ipv6:
enabled: true
set-only: false
table: crowdsec6
chain: crowdsec6-chain
enabled
true|false
Enable or disable ipv4 or ipv6
set-only
true|false
If set-only is set to true, the component will only manage the set contents.
table
string
Name of the nftables table
chain
string
Name of the nftables chain
Manual installation
Assisted
First, download the latest crowdsec-firewall-bouncer release.
$ tar xzvf crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.tgz
$ sudo ./install.sh
From source
Run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/crowdsecurity/cs-firewall-bouncer.git
cd cs-firewall-bouncer/
make release
tar xzvf crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.tgz
cd crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-v*/
sudo ./install.sh
Upgrade
If you already have crowdsec-firewall-bouncer installed, please download the latest release and run the following commands:
tar xzvf crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.tgz
cd crowdsec-firewall-bouncer-v*/
sudo ./upgrade.sh
Configuration for manual installation
To be functional, the crowdsec-firewall-bouncer service must be able to authenticate with the local API.
The install.sh script will take care of it (it will call cscli bouncers add on your behalf).
If it was not the case, the default configuration is in /etc/crowdsec/bouncers/crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.yaml.
You can then start the service:
sudo systemctl enable --now crowdsec-firewall-bouncer
If you need to make changes to the configuration file and be sure they will never be modified or reverted
by package upgrades, starting from v0.0.25 you can write them in a crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.yaml.local file as described in
Overriding values.
Package upgrades may have good reasons to modify the configuration, so be careful if you use a .local file.
logs
logs can be found in /var/log/crowdsec-firewall-bouncer.log
modes
- mode
nftablesrelies on github.com/google/nftables to create table, chain and set. - mode
iptablesrelies oniptablesandipsetcommands to insertmatch-setdirectives and maintain associated ipsets - mode
ipsetrelies onipsetand only manage contents of the sets (they need to exist at startup and will be flushed rather than created) - mode
pfrelies onpfctlcommand to alter the tables. You are required to create the following tables on yourpf.confconfiguration:
# create crowdsec ipv4 table
table <crowdsec-blacklists> persist
# create crowdsec ipv6 table
table <crowdsec6-blacklists> persist
You can refer to the step-by-step instructions of the user tutorial on FreeBSD to setup crowdsec-firewall-bouncer with pf.
ipset
ipset lists have to exist before crowdsec-firewall-bouncer starts. You can create them and add them to your iptables like this:
ipset create crowdsec-blacklists hash:ip timeout 0 maxelem 150000
ipset create crowdsec6-blacklists hash:ip timeout 0 family inet6 maxelem 150000
iptables -I INPUT 1 -m set --match-set crowdsec-blacklists src -j DROP
ip6tables -I INPUT 1 -m set --match-set crowdsec6-blacklists src -j DROP




